Technical information
Boiler assembly diagram, when electrolytic the ion boiler is connected as an additional heating device

Boiler assembly diagram, when electrolytic the ion boiler is connected as an additional heating device with radiators

Boiler assembly diagram, when electrolytic the ion boiler is connected as an additional heating device with underfloor heating

Boiler assembly diagram, when electrolytic the ion boiler is connected as an additional heating device with radiators and underfloor heating
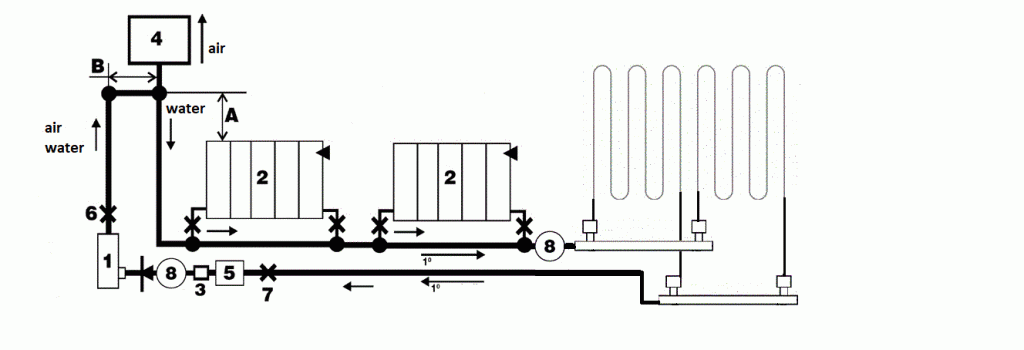
- 1. Electrode ion boiler
- 2. Radiator
- 3. Sensor – thermostat
- 4. Closed expansion vessel
- 5. Filter
- 8. Circulation pump
- 9. Underfloor heating
- X. Ball valve

The boiler is the main element of the heating system, which transfers the heat energy generated by the combustion of fuel into the common heating system. How to choose the boiler correctly? When selecting a boiler you should know the heat loss of the building , the heat demand for hot water and ventilation (if such a system is provided). Therefore, drawings of the heated building with a description of the premises are required for the selection of the boiler. The boiler output is selected according to the volume of the heated premises. By default, 10 square meters and 2.5 meters in height uses 1 kW for heating. However, the buildings differ in their thermal resistance, so it is worthwhile to entrust the power calculation to a specialist. To compensate for the heat loss and other heat needs of the building, it is accepted to add about 20-30% of additional power. Hot water preparation uses about 25% of power, but in some cases the space heating is disconnected during water heating, which almost does not change the room temperature.
The summarized data on the performance of electric boilers are taken from the records kept at the objects where the electric boilers and electric heating element boilers were installed.

The following requirements must be met with the utmost precision:
The boiler entry temperature (sensor) must be between 150 C and 200 C. Boiler start time is not longer than 30 seconds.
Making an adjustment:
Turn on the boiler and after 30 seconds when the heat carrier temperature reaches 150 – 200 C measure the starting (standard) current with an ammeter. The starting current must be within the parameters specified in the table.

Heating of the heat carrier in an electrode (ionic) boiler takes place by direct conversion of electricity into thermal energy. The electric current splits the water molecules in the boiler into positively and negatively charged ions, which move towards the positive and negative electrodes respectively, releasing energy, so that the water is heated directly, without any mediator (eg heating element). Once connected to the electrical grid, the boiler heats up almost immediately – after just a minute, the water temperature in the outlet pipe reaches 40 – 55º. As the water heats, its specific resistance decreases. The boiler gradually accumulates electronic power and converts it to water in the form of heat. The nominal capacity of the boiler will depend on the water temperature selected by the user and the amount of water in the system.
© 2023 All rights reserved.

